| [1] 余丕军,王露萍,郭好,等.胶原蛋白—壳聚糖复合纳米纤维膜用于皮肤缺损的修复[J].中国工程组织研究与临床康复,2011,15(51): 9561-9564.
[2] 田康爱,梁玉.糖尿病皮肤病变研究进展[J].天津医科大学学报, 2011,17(3):431-434.
[3] Yomnglshi S.Advanced glycation end products and neceptor-o-idative stress system in diabelie vascular complication.Ther Apher Dial.2009;13(6):534.
[4] 朱晓璐,孙嘉.生长因子治疗糖尿病足溃疡的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2012,7(2):63-65.
[5] 刘如俊,赵文志,张路,等.表皮生长因子在糖尿病足溃疡创面愈合过程中的作用观察及其机制探讨[J].大连医科大学学报, 2014, 36(4):322-327.
[6] Broughton G 2nd,Janis JE, Attinger CE.The basic science of wound healing.Plast Reconstr Surg.2006;117(7 Suppl): 12S-34S.
[7] 何月勇,张蓓,王姣姣,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在2型糖尿病难治性慢性溃疡患者中的临床应用[J].中国医师锦绣杂志, 2014, 37(10):66-68.
[8] 付坤,柳景华.成纤维细胞生长因子21在糖脂代谢中的研究进展[J].中华老年心血管病杂志,2014,16(5):550-553.
[9] 贾乐宁,程飚,苏磊.重组人血小板源生长因子促进糖尿病大鼠创面愈合机制的初步研究[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(32): 7194-7196.
[10] 袁南兵,龙洋,张祥迅,等.自体富血小板凝胶治疗糖尿病难治性皮肤溃疡作用机制的初步探讨[J].四川大学学报,2009, 40(2): 292-294.
[11] 吴维,胡何节,邓福生,等.血管内皮细胞生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子体外联合诱导外周血单个核细胞定向分化为血管内皮细胞 [J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(11):2094-2097.
[12] 刘移峰,刘德伍,郭光华,等.重组人粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子对糖尿病大鼠创面愈合及微小RNA表达的影响[J].中华烧伤杂志,2014,30(3):243-250.
[13] Singh V,Devgan L,Bhat S,et al.The pathogenesis of burn wound conversion.Ann Plast Surg,2007;59(1):109-115.
[14] 彭艳阳,吴伟,曾丽娜,等.重组人表皮生长因子和碱性成纤维生长因子促进人角膜上皮细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(7):1045-1050.
[15] 张晓林.重组人表皮生长因子治疗皮肤创面的临床效果观察[J].中原医刊,2003,30(3):13-14.
[16] 朱建辛,张耀明.重组人表皮生长因子在慢性溃疡中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(1) :42-43.
[17] Tanii M,Yonemitsu Y. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor(EGF) to enhance healing for diabetic foot ulcers.Circ Res.2006;98:4-6.
[18] 肖斌,刘毅.以脂肪源性干细胞膜片构建组织工程皮肤[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(33):5361-5365.
[19] 孙传伟,陈华德,卞微宁,等.脂肪来源间充质干细胞移植对大鼠全层皮肤缺损的修复作用[J].广东医学,2014,35(6):805-808.
[20] 陆伟,金岩,张勇杰,等.脂肪组织来源干细胞复合胶原构建组织工程皮肤修复皮肤缺损[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2007,23(2): 161-164.
[21] 何丽娟,刘大庆,白慈贤,等.自体BMSCs复合胶原膜修复猪全层皮肤缺损[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(3):348-352.
[22] 卢晓林,徐青峰,童昕,等.胶原膜复合碱性成纤维细胞生长因子修复皮肤缺损的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2014,30(7):630-634.
[23] 毛淑芳.皮肤组织工程支架材料的研究进展[J].上海化工, 2014, 39(3):27-30.
[24] Varga M,Sixta B,Bem R,et al.Application of gentamicin-collagen sponge shortened wound healing time after minor amputations in diabetic patients -a prospective, randomised trial.Arch Med Sci.2014;10(2):283-287.
[25] 曹石金,何朝辉,李逊,等.糖尿病大鼠模型的[J].解剖学研究, 2012, 34(4):295-298.
[26] 刘京珍,叶英.不同剂量链脲佐菌素建立糖尿病大鼠模型稳定性观察[J].徐州医学院学报,2013,33(5):305-307.
[27] 徐叔云,卞如濂,陈修.药理学实验方法学[M].北京:人民卫生出报社,2002:1517-1522.
[28] 武志强,丁越,张力平,等.组织工程口腔黏膜固有层修复皮肤缺损的初步研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(2):172-176.
[29] 蒋朝辉,杨国珍.高糖高脂饮食结合链脲佐菌素建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型的改良[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2011,21(1):19-22.
[30] Rakieten N,Rakieten ML,Nadkarni MV.Studies on the diabetogenic action of streptozotocin(NSC-37917).Cancer Chemother Rep.1963;29(7):91-98.
[31] Bailes BK. Diabetes mellitus and its chronic complications. AORN J.2002;76(2):266-276.
[32] 徐建华,孙中华,颜燕,等.应用于保健食品功能学评价的糖尿病动物模型研究[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2002,12(6):668-669.
[33] Rossini AA,Williams RM,Appel MC,et al.Sex difference in the multiple-dose streptozotocin model of diabetes. Endocrinology. 1978;103(4):1518-1520.
[34] Merdes JP,Willy MS.Influence of age and sex on inseptibity to STZ diabetes.Diabetes.1980;29(Suppl 2):132.
[35] Mikesh LM,Aramadhaka LR,Moskaluk C,et al.Proteomic anatomy of human skin.J Proteomics. 2013,84:190-200.
[36] 姚东刚,张选奋. IV、VI、XII、XIV、XVI型胶原与皮肤创伤修复及瘢痕增生的关系[J].中国美容医学,2014,23(6):507-511.
[37] 牛轶雯,缪明远,曹晓赞,等.大鼠全层皮肤缺损创面愈合过程中巨噬细胞浸润及表型研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2014,30(2):109-115.
[38] 黄昕,沈向前,吴守成,等.糖尿病裸鼠的皮肤组织改变及其创面愈合的相关性[J].上海交通大学学报,2012,32(1):59-63.
[39] 朱伟,张晓莉,刘洋,等.鱼鳞胶原蛋白对免疫低下小鼠皮肤伤口愈合的影响[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2014,48(3):177-181.
[40] 李晓光,方勇.创面愈合过程中血管新生的机制和过程[J].中华整形外科杂志,2010,26(6):477-480.
[41] 徐阳,张进,王文岭,等.胶原贴敷料对点阵激光术后皮肤修复作用的临床评价[J].实用皮肤病学杂志,2014,7(2):104-109.
[42] 陈雪,刘娟,杨高云.胶原贴敷料的临床应用[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2010,9(23):1823-1827.
[43] 张莹,张朝栋.胶原贴敷料治疗接触性皮炎的临床观察[J].皮肤病与性病,2012,34(1):37.
[44] 曲永红,曲晓娟.胶原贴敷料配合中药湿敷治疗座疮120例[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2007,9(1):115.
[45] 孙继伟,韦旭,邸鸿雁,等.胶原贴敷料联合异维A酸红霉素凝胶治疗寻常座疮疗效观察[J].中国麻风皮肤病杂志,2014,30(9):523.
[46] 王世岭,邓诗琳,马建丽,等.不同剂型重组人表皮生长因子对烧伤创面促愈合作用比较[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2002,18(1):12-14.
[47] 安宏元,陈杰翔.重组人表皮生长因子不同剂型作用于糖尿病溃疡动物模型的疗效比较[J].中国现代医药杂志,2010,12(10): 82-85. |
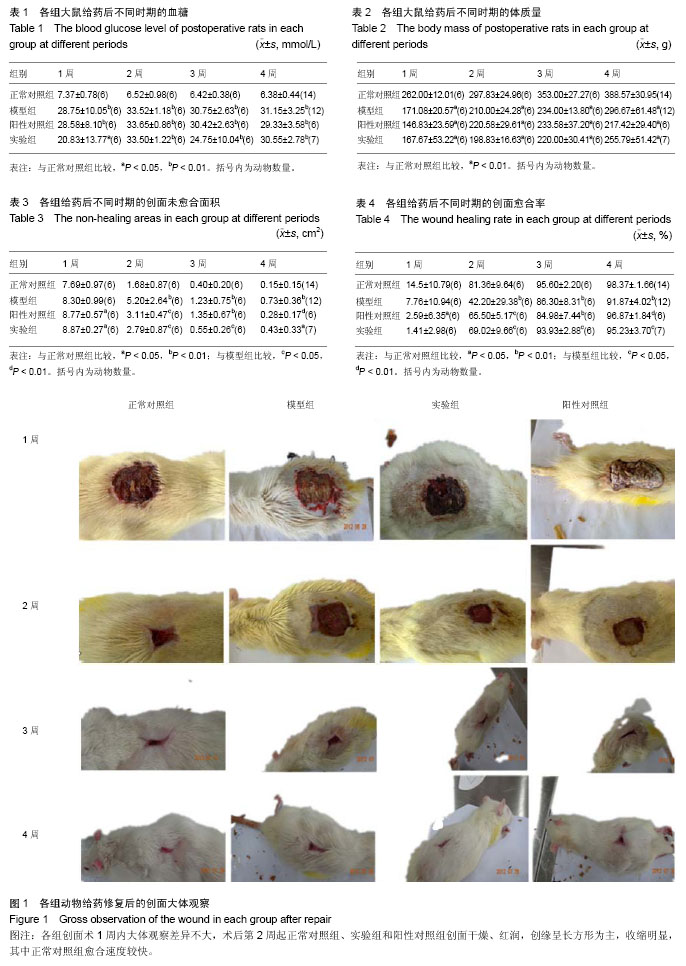
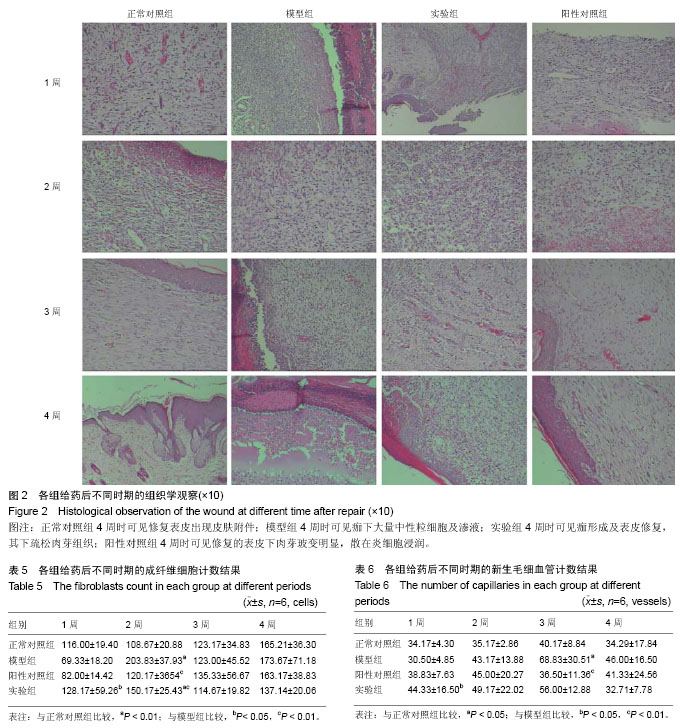
.jpg)